Our country pages
Africa
Europe
Search
Order a sample
You can order up to 3 free sample tiles.
We'll aim to deliver your sample order within 5-7 working days from your order date.
Radon Barrier Protection Strategy
Inside buildings the air pressure tends to be lower than pressure levels outside. This is due to a combination of wind and temperature differences. The result is that radon soil gas and air are drawn into buildings through the many small gaps and cracks formed during, and after, construction, e.g. in solid floors and walls at ground level, through construction joints and around service pipes.
Radon, Air and Moisture is excluded from buildings using passive protection measures. Radon can also be removed using active protection.
Jump to section
Best Practice - Radon Sumps
Best Practice - Radon Sumps
You should make provision for subfloor depressurisation by installing a radon sump/s and network of pipes during construction as highlighted in the Irish Building Regulations 1997- 2008 Technical Guidance Document C (Section 2).
Sub-floor depressurisation, also called sub-slab suction, is a most effective way of reducing radon levels should the need arise at any time over the lifecycle of a building.
By installing a radon sump under a ground floor slab a void is provided from which radon can be drawn by use of an extractor fan; this lowers the sub-floor air pressure relative to that indoors. The radon gas is sucked from below the floor and vented by an external pipe to the air above the building. The radon is quickly diluted and will cause no further harm to health.
As radon levels are generally established when a building is completed and may alter over its lifecycle due to change of use e.g. the reduction of ventilation or the addition of extensions, the installation of a radon sump and pipework at construction stage is easy and inexpensive and a useful precaution even if never used.
Note: The radon sump and pipework do not provide any radon removal until a fan is fitted to an external vent pipe, and the system is activated.
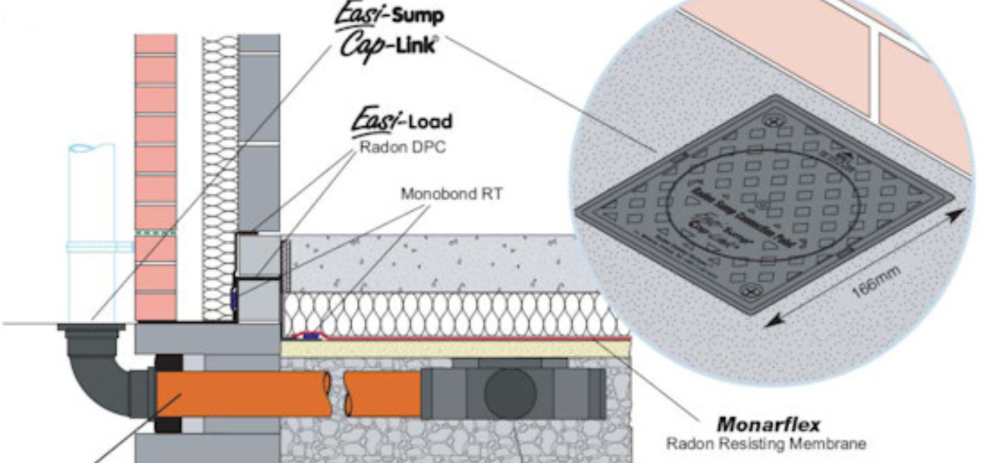
The Easi-Sump provides the void under the ground floor slab from which radon soil gas can be extracted.
And at ground level outside the building the Easi-Sump Cap-Link terminates, and securely caps, the pipework leading from the sub-floor Easi-Sump. It is the ‘clearly identifiable’ Radon Sump Connection Point should the extraction system ever need to be extended above roof level and activated in the future.
Key Components: You should use an Easi Sump & Easi-Sump Cap-Link which are certified by NSAI Agrément Board Certificate No. 09/0238.
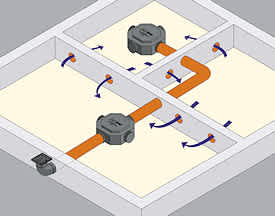
What you do if you need to activate the radon soil gas protection system.
High radon soil gas levels can be reduced at any time
If, at any stage throughout the lifecycle of the building, you need to take action to reduce high radon soil gas levels, this can be readily achieved by extending the pipework which terminates in the Easi-Sump Cap-Link to a new termination point above the building.
An in-line extractor fan is installed and when this is activated the radon soil gas is diluted harmlessly into the atmosphere above the building.
You’ll find that a circular section of the Easi-Sump Cap-Link cover can be removed on site to install the Radon Vent Pipe. A central drill locator mark in the cover of the Easi-Sump Cap-Link facilitates removal. This cut-out section is of sufficient size to accept a 110mm PVC-U standard pipe. Once you connect the external RVP, with in-line fan, to the Easi-Sump Cap-Link the link to the sub-floor pipework and Easi-Sump is completed
Key Component: You should connect an external Radon Vent Pipe (RVP) with an in-line extractor fan to the Easi-Sump Cap-Link which has been installed during construction at ground level outside the building.